If you’ve been watching motion tracking evolve over the past few years, you know the technology has come a long way. What once required million-dollar setups now fits into compact, affordable devices. And by 2026, even more industries will have access to it.
Here at Movea Tech, we’ve spent years testing motion control systems and tracking how this technology evolves. We’ve seen what works, what fails, and where the real opportunities are.
This guide breaks down five industries set to benefit most from motion tracking in 2026: gaming, healthcare, robotics, automotive, and training simulations. You’ll see real applications, practical benefits, and what’s driving adoption across these sectors.
So by the time you’re done reading, you’ll understand exactly where this technology is going and which industries are leading the way.
The global motion capture market is on track to reach $5.7 billion by 2033, and gaming is leading that charge.
As information and communications technology advances, players expect more immersive experiences. And studios are responding by investing heavily in tracking technologies that create lifelike interactions.
Two areas stand out in particular: VR gaming and film production.
Full-body tracking lets players physically interact with virtual worlds instead of relying on controllers alone. Your movements, from a simple wave to a full jump, get translated into the game in real time.
Through our testing of motion capture systems, we’ve seen how much VR headsets have improved. They now pair with motion sensors to pick up on gestures, head tilts, and hand movements with impressive accuracy.
Film studios use motion capture to create realistic CGI characters while cutting production time significantly. Tools like Premiere Pro and Mocha AE help editors refine tracking data in post-production. And the result is smoother animation and faster turnaround on visual effects.
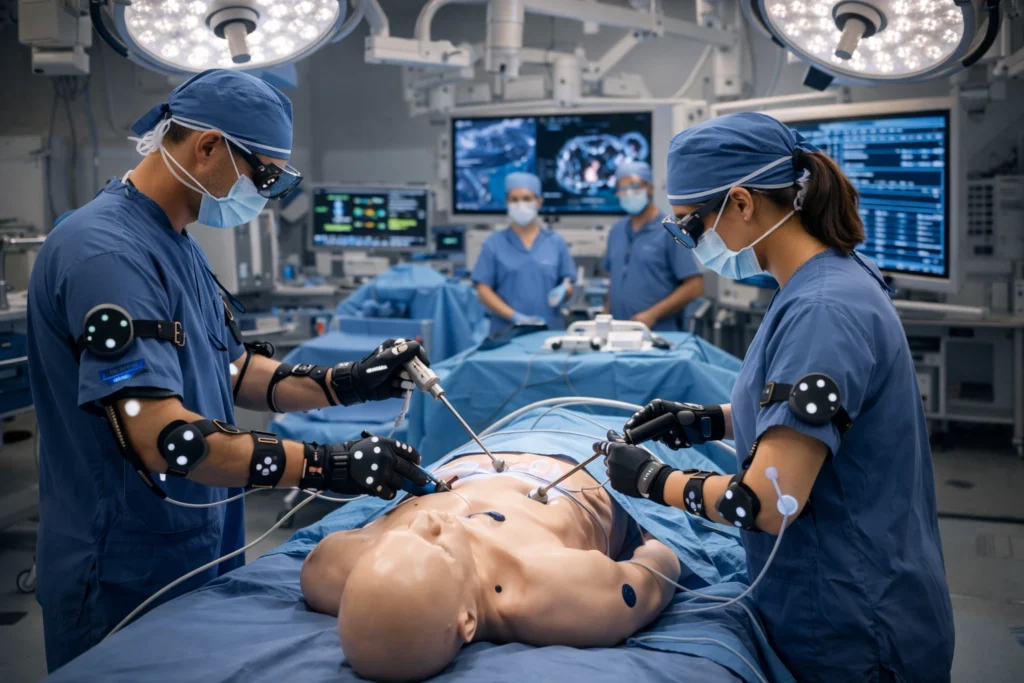
The biggest win for healthcare is precision. Motion tracking gives doctors and therapists real data instead of guesswork. This shift is helping to drive innovation across rehabilitation, surgery, and early diagnosis.
Because of this, physical therapists now use tracking technologies to monitor how patients move during recovery. They can measure angles, speed, and range of motion with accuracy that the human eye simply can’t. And this kind of data supports better treatment plans and faster progress overall.
Believe it or not, surgeons are also practicing complex procedures in virtual environments before performing them on real patients. In our experience reviewing medtech trends, surgical simulation has quietly become a standard part of training at many hospitals.
Beyond surgery, wearable sensors help doctors detect early signs of mobility issues in elderly patients. Scientific research in this area continues to grow, with a clear focus on human well-being and sustainable care models.
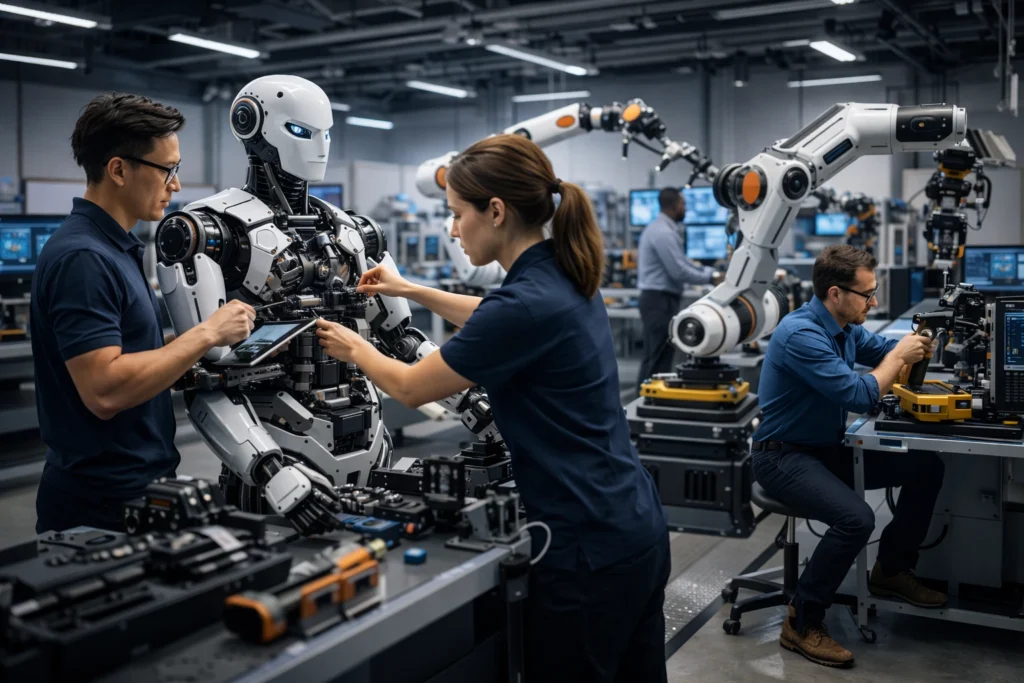

What if a factory could spot a robot malfunction before it even happens? That’s exactly what motion tracking enables on modern production floors. As industries push toward sustainable industrialization, tracking technologies are becoming essential for building resilient infrastructure that can adapt to changing demands.
Here’s how manufacturers are putting this to work:
With these tools in place, manufacturers can build resilient infrastructure that supports long-term growth and efficiency.
For drivers, motion tracking means safer roads and more convenient controls without lifting a finger. By combining global positioning systems with motion sensors, vehicles can now respond to both location data and physical gestures in real time.
There are three major ways this makes driving easier:
As these technologies mature, expect infrastructure upgrades that support smarter, safer transportation networks.
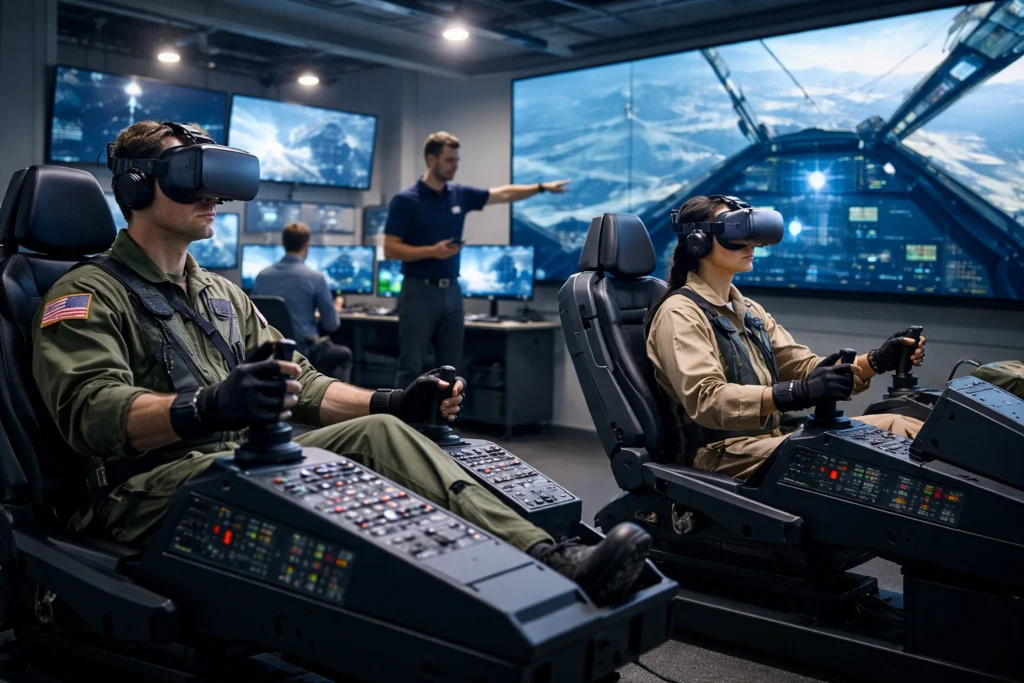

Training simulations use motion tracking to recreate high-pressure environments where mistakes don’t cost lives. From military drills to emergency response, organizations are using these tools to support domestic technology development and prepare personnel for real-world challenges.
The two fields that are seeing the biggest gains include:
Military and aviation programs have long relied on motion-tracked simulations to train personnel in realistic scenarios. Pilots practice emergency landings, while soldiers rehearse combat situations, all without real-world consequences.
These programs also support domestic technology development by encouraging local research and innovation. In many developing countries, governments are investing in simulation technologies to train their defense forces without relying on expensive imported systems.
Medical students now practice surgeries in virtual labs where their hand movements are tracked and evaluated. This gives instructors clear data on technique, precision, and areas that need improvement.
Emergency responders benefit from similar setups. They rehearse rescue operations with full-body tracking to improve coordination and response times. When a real crisis hits, teams that have trained in simulations tend to react faster and make fewer errors.
Now that you’ve seen how different industries are using this technology, the next question is: why now?
Hardware costs have dropped significantly over the past five years. This means mid-sized businesses and startups can now afford tracking technologies that once belonged only to large corporations.
Open-source software and developer-friendly APIs are also encouraging innovation and speeding up greater adoption across industrial sectors.
Beyond cost, there’s a global push for affordable and equitable access to these tools. Developing countries and least developed countries are investing in sustainable industrialization to support economic development.
And the result is industrial diversification on a scale we haven’t seen before.
Motion tracking is no longer reserved for Hollywood studios or high-end research labs. By 2026, industries like gaming, healthcare, robotics, automotive, and training simulations will rely on it even more heavily.
The technology keeps getting smaller, cheaper, and more accurate. And as access expands to developing countries and smaller businesses, we’ll see even more creative applications emerge.
If your industry isn’t exploring motion tracking yet, now is a good time to start paying attention. Because the companies that adopt early will have a clear advantage when this technology becomes the standard.